The crimping process is the core of ensuring stable current transmission in automotive wiring harnesses. Its quality must meet three major standards: 100% metal cladding rate, no damage to the conductor, and no deformation of the terminal. Through cold pressing with molds, the terminal and conductor form a metal interlocking structure, ensuring that the copper wire is completely wrapped and evenly distributed. The crimping area is smooth and firm, capable of withstanding over 1000 vibration tests.
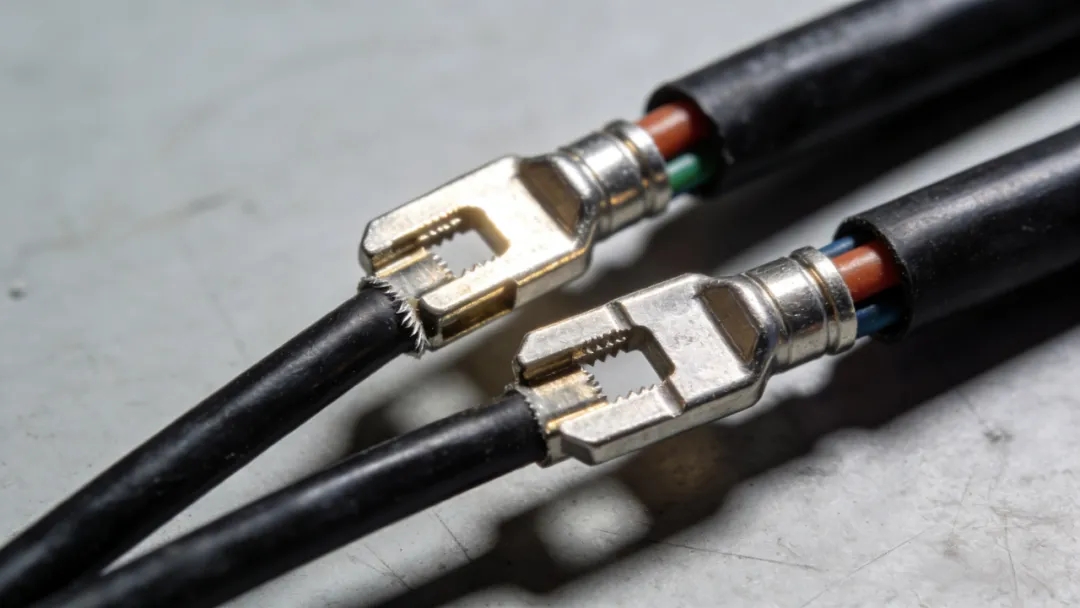
If the crimp height deviation exceeds 0.2mm or the mold is worn, defects such as copper wire exposure and breakage are prone to occur, leading to a 3-5 times increase in contact resistance, which can cause localized heating and even fire risks. There have been recalls of electric vehicles due to contact failures caused by poor crimping.
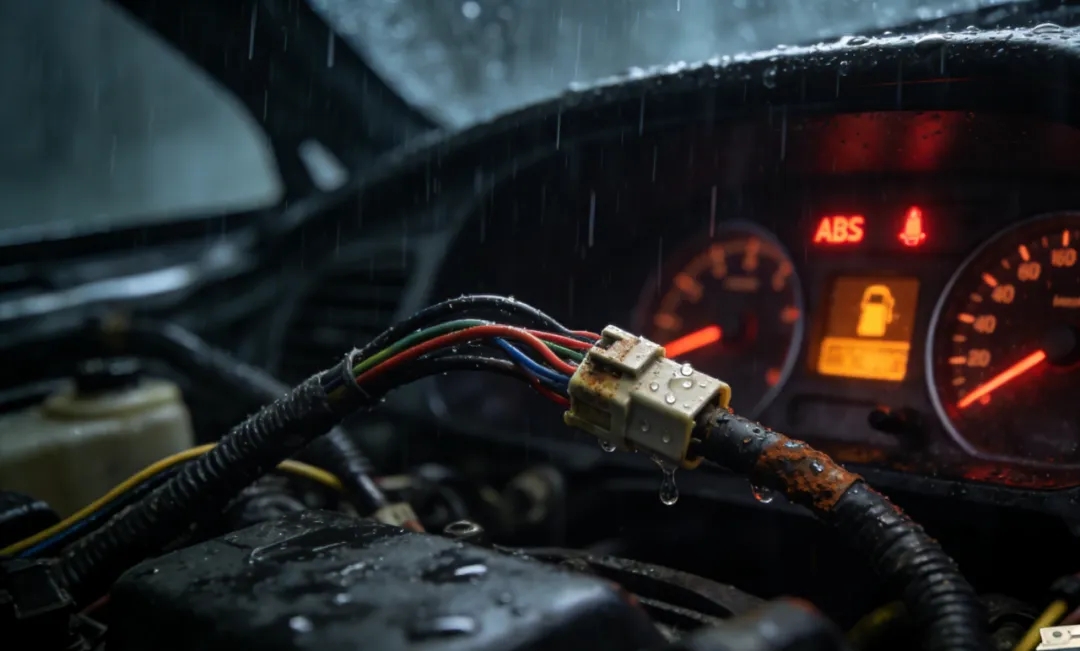
The waterproof rating serves as a crucial safeguard for wiring harnesses in complex environments. Wiring harnesses compliant with the IPX7 standard employ a triple-layer design consisting of sealing rings, waterproof plugs, and corrugated tubes, ensuring internal dryness even after being immersed in water up to a depth of 1 meter for 30 minutes. The waterproof plugs retain their elasticity within the temperature range of -40°C to 125°C, while the corrugated tubes effectively absorb shock and resist wear.
When waterproofing is inadequate, moisture is prone to infiltrate the wiring harness, causing oxidation of wires, signal delay, and in severe cases, short-circuiting of the ECU. For example, a certain SUV experienced a vehicle stall due to rainwater infiltration caused by the aging of the waterproof plug in the door wiring harness.
Crimp connection and waterproofing jointly establish safety redundancy for electrical systems. In high-temperature areas such as the engine compartment, the wiring harness must possess both high pull-out strength (≥200N) and IPX9K waterproof rating; in the chassis area, it must pass salt spray testing and resist gravel and sediment. High-voltage wiring harnesses for new energy vehicles also require impedance ≤50μΩ, and are equipped with a shielding layer and flame-retardant waterproof sheath to prevent electromagnetic interference and electric leakage.

Using fully automatic crimping equipment (with an accuracy of ±0.01mm) and wire harnesses certified by IPX8, the failure rate can be reduced to 1/20 of that of manual crimping. With the development of intelligent driving, "smart wire harnesses" may be able to monitor the crimping status in real time in the future, further enhancing safety.
The wiring harness is like an "invisible guardian" of a car, and its millimeter-level craftsmanship and rigorous waterproof testing are directly related to the safety and reliability of the entire vehicle.
Special statement: The content is sourced from "Wire Harness World" for reference only, aiming to disseminate more information rather than for profit. The copyright belongs to the original author. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal.

